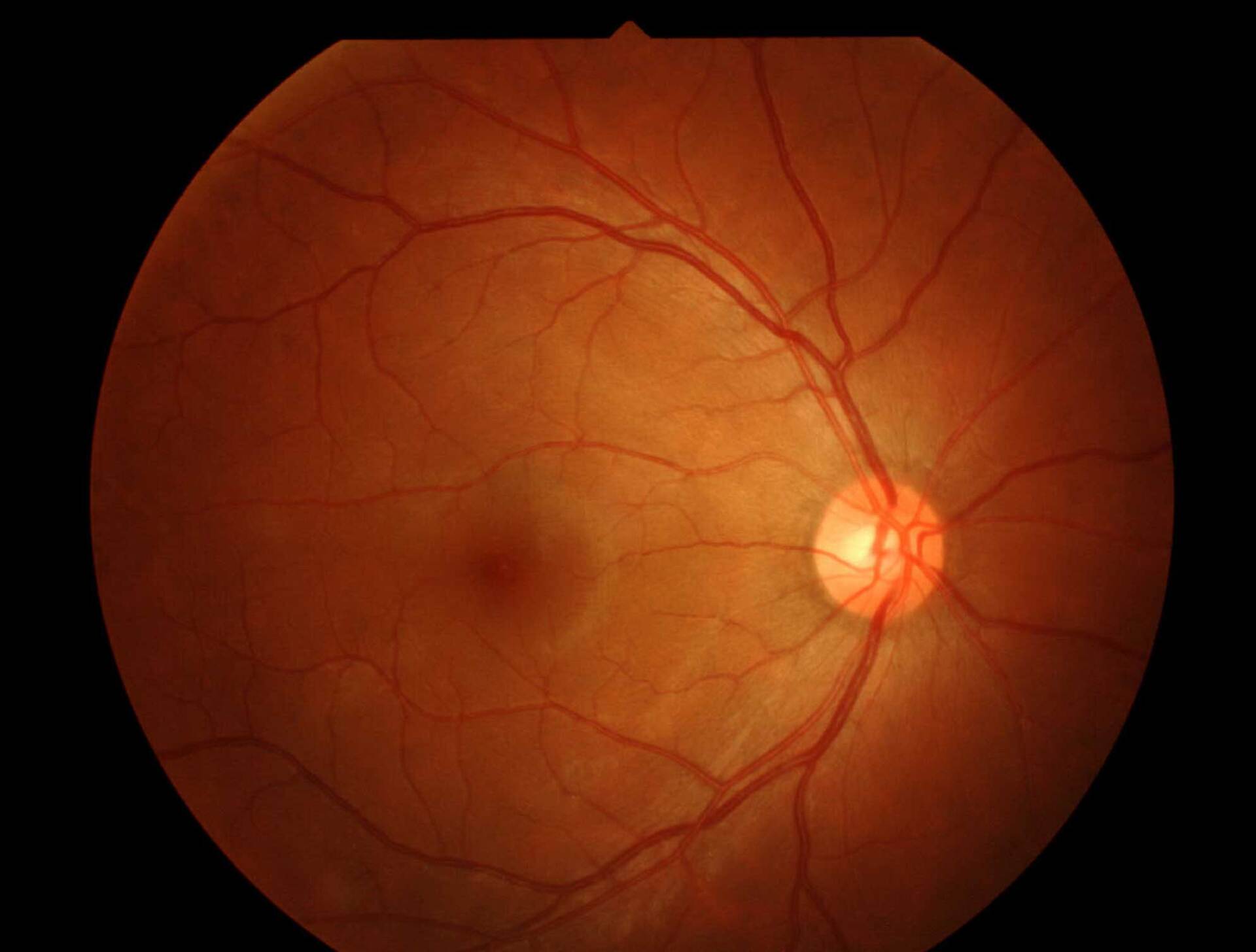
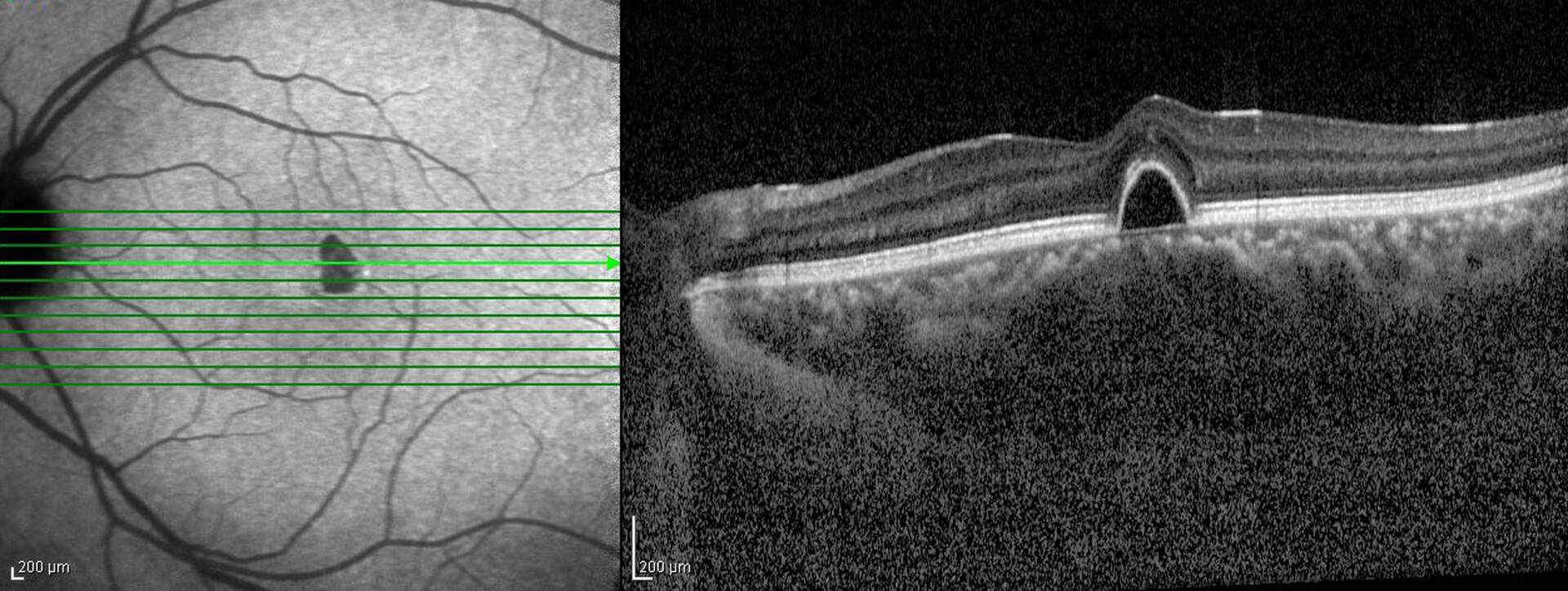
Optical coherence tomography (OCT) is a non-invasive imaging technology used to accurately identify potential eye issues by taking high-resolution cross-sectional images of the retina. OCT is similar to ultrasound testing, except that the imaging measures light rather than sound. It is a way for us to inspect the back of the eye, including the macula, optic nerve, retina, and choroid.
We can view the back of the eye during an eye examination, but sometimes we need to inspect further or capture more detail below the surface, which standard techniques don’t do. In some ways, it’s comparable to doing an "MRI of the retina." Some describe it as an optical ultrasound because it images reflections between tissues to provide doctors with cross-sectional images.
Optical coherence tomography works by using interferometry, enabling eye care professionals to image tissue with light instead of X-rays, sound or radiofrequency. It works by shining a beam of light into the eye. Different tissues reflect part of this light, and images are built based on this internal reflection differential.
An OCT images to approximately 2-3 mm below the surface of the tissue. Images are obtained clearly through a transparent window, such as the cornea. The light that emits into the eye is safe. The output is near-infrared light so that no eye damage will occur.